Word2Vector
20 Oct 2018
Word2Vec
In the past, “one hot encoding” was the orthodox method in Natural Langauge Processing when transforming text data into processable numeric data. The one-hot encoding method represents categorical data into numerical data by generating standard unit vectors. $N$ words will generate corresponding $n$ n-dimensional standard unit vectors.
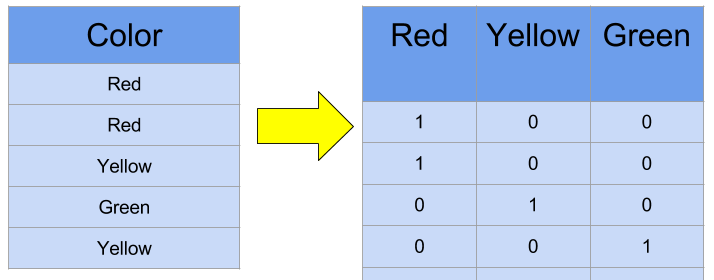 However, this type of encoding cannot reflect semantic and relational meaning between respective words. In other words, It cannot represent or imply the similarity of words. Moreover, increase in the number of words will expand the dimension which will eventually lead to complex computation, because one hot encoding only uses the axis of n-dimension.
To overcome these limitations, there has been numerous approaches to apply semantical meaning and reduce dimension. Some of the methods include: NNLM, RNNLM, CBOW, Skip-gram.
However, this type of encoding cannot reflect semantic and relational meaning between respective words. In other words, It cannot represent or imply the similarity of words. Moreover, increase in the number of words will expand the dimension which will eventually lead to complex computation, because one hot encoding only uses the axis of n-dimension.
To overcome these limitations, there has been numerous approaches to apply semantical meaning and reduce dimension. Some of the methods include: NNLM, RNNLM, CBOW, Skip-gram.
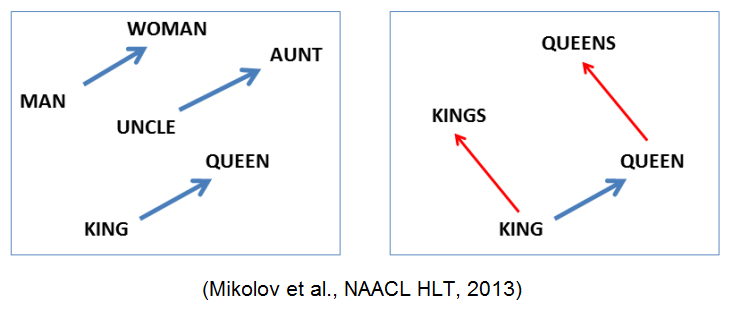 One hot coding is a Sparse Representation, which indicates that majority of elements are 0 in matrix or vector. As an alternative way, Distributed Representation or Dense Representation was used to embed semantic of words to vector. This process is called “embedding”. Words represented by these methods and went through embedding process is called embedding vector.
As word2vec adopts distributed representation, it assumes the distributional hypothesis. The assumption is that “words with similar position have similar meanings”. Word2Vec suggests two network models to train data. One is CBOW( continuous bag of words) model and the other is Skip-gram model.
One hot coding is a Sparse Representation, which indicates that majority of elements are 0 in matrix or vector. As an alternative way, Distributed Representation or Dense Representation was used to embed semantic of words to vector. This process is called “embedding”. Words represented by these methods and went through embedding process is called embedding vector.
As word2vec adopts distributed representation, it assumes the distributional hypothesis. The assumption is that “words with similar position have similar meanings”. Word2Vec suggests two network models to train data. One is CBOW( continuous bag of words) model and the other is Skip-gram model.
CBOW Model (Continiuous Bag of Words) & Skip-gram Model
CBOW uses surrounding words(context words) to predict the words in the middle (center words), while Skip-gram model uses center words to predict surrounding words. Simply saying, CBOW is answering to a question of “given a set of these context words, what missing word (center word) is likely to appear at the same time?”. Skip-gram is answering to a question of “given this one word, what are the other words that are likely to appear at the same time?”. Both methods are supervised learning, training the Word2Vec model with corpus data.

references
- https://wikidocs.net/22660 (NLP introduction using Deep Learning)
- https://shuuki4.wordpress.com/2016/01/27/word2vec-%EA%B4%80%EB%A0%A8-%EC%9D%B4%EB%A1%A0-%EC%A0%95%EB%A6%AC/
