Spearman Correlation
12 Oct 2018
Correlation
Correlation is a concept that is used to measure the association between variables, whether they are related or not. If the variables are related examining whether the relationship is positive or negative, or whether a specific model can explain the relationship. (Linear, non-linear)
For example, pearson correlation measure the “linearity” of two continuous variables, assuming that the two variables follow normal distribution.
Spearman Correlation ($\rho$)
-
Spearman’s Correlation measures the correlation between two variables, taking their rankings into account. It evaluates the variables in a non-parametric way; meaning that it uses statistical method where data is not required to follow a normal distribution. In other words, Spearman correlation does not assume anything about the distribution of data.
- The assumption required for Spearman correlation are that:
- the data must be at least ordinal
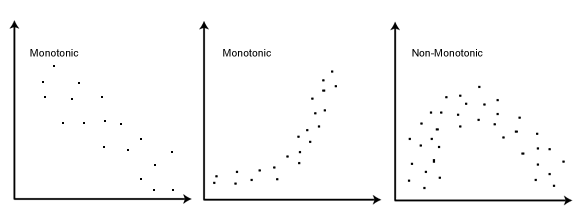
- the scores on one variable must be monotonically related to the other variable.
- The correlation is calcuated as a following equation: $\rho = 1 - \frac{6 \sum d_{i}^{2}}{n(n^{2}-1)}$
- $\rho$ : Spearman rank correlation
- $d_i$ : the difference between the ranks of corresponding variables
- $n$ : number of observations
Interpreting the value of Spearman Correlation
-
The Spearman correlation coefficient can take values from +1 to -1 \(( -1 < \rho < +1)\)
-
+1 indicates a perfect association of ranks, while -1 indicates a perfect negative association between ranks. The closer value to 0, implies the weaker association between the ranks.
